A Histogram Which Is Left Skewed Has the Following Property
In other words if you fold the histogram in half it looks about the same on both sides. A s 5983 IQR 845.
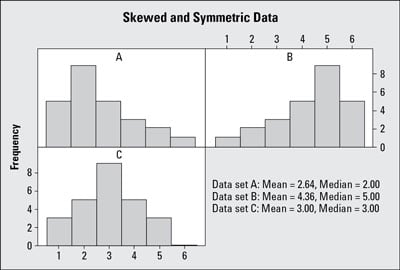
How To Identify Skew And Symmetry In A Statistical Histogram Dummies
For example if a procedure initially has a lot of.

. A right-skewed distribution usually occurs when the data has a range boundary on the right-hand side of the histogram. A distribution is left skewed if it has a tail on the left side of the distribution. A distribution skewed to the left is said to be negatively skewed.
Lifetime in hours Number of lamps. Want to see the full answer. While normal distribution is the most commonly encountered type of distribution examples of the negatively skewed distributions are also.
Thats because there is a long elongated tail in the negative direction. The following table gives the lifetime of 400 neon lamps. A histogram is left skewed if it has a tail on the left side of the distribution.
For example a boundary such as 100. Big on right 2. The right-hand side seems chopped off compared to the left side.
In a left-skewed distribution a large number of data values occur on the right side with a fewer number of data values on the left side. The data are symmetric. If the data are symmetric they have about the same shape on either side of the middle.
The mean is 63 the median is 65 and the mode is seven. Some histograms will show a skewed distribution to the left as shown below. The histogram has vertical bars of width 5 starting at the horizontal axis value of 35.
The above histogram is for a distribution that is skewed right. 8 is not symmetrical. Chapter 2 Problem 5CR.
Skewed distributions bring a certain philosophical complexity to the very process of estimating a typical value for the distribution. A histogram in which most of the data falls to the right of the graphs peak is known as a right-skewed histogram. The following graph represents the exam scores of 17 students and the data are skewed left.
The histogram for the data. The following frequency histogram presents the numbers of trials it took each rat to learn the maze. A skewed left histogram is a histogram that is skewed to the left.
Mean is located on the right side of the curve mode close to the peak median located in between. Skewness is a way to describe the symmetry of a distribution. So if the data sets lower bounds are extremely low relative to the rest of the data this will cause the data to skew right.
They are also known as negatively skewed distributions. All 3 are not the same number. A Determine the standard deviation and interquartile range of the data.
A distribution is called skewed left if as in the histogram above the left tail smaller values is much longer than the right tail larger values. A histogram is skewed to the left if most of the data values fall on the right side of the histogram and a histogram tail is skewed to left. A right-skewed histogram has a definite relationship between its mean median and mode which can be written as mean median mode.
Skewed to the right. Data skewed to the right is usually a result of a lower boundary in a data set whereas data skewed to the left is a result of a higher boundary. When data are skewed left the mean is smaller than the median.
Note that left skewed distributions are sometimes called negatively-skewed. Another cause of skewness is start-up effects. In statistics a negatively skewed also known as left-skewed distribution is a type of distribution in which more values are concentrated on the right side tail of the distribution graph while the left tail of the distribution graph is longer.
What property does this illustrate. We are asked to describe if the histogram of our data is skewed or symmetrical. It is the histogram where very few large values are on the left and most of the data are on the right side such data are said to be skewed to the left.
5 Examples of Negatively Skewed Distributions. A histogram is said to be skewed to the left longer tail to the left tabular method that can be used to summarize data on 2 variables crosstabulation. Right skewed histogram.
This is the case because skewed-left data have a few small values that drive the mean downward but do not affect where the exact middle of the data is that is the median. For a distribution that is skewed left the left whisker is _____ the right whisker. A skewed left distribution is one in which the tail is on the left side.
A histogram is right skewed if it has a tail on the right side of the distribution. The approximate heights of the bars are as follows where the horizontal axis label is listed first and the approximate height is listed second. Skewed to the left 2.
Note that in a skewed left distribution the bulk of the observations are mediumlarge with a few observations that are much smaller than the rest. A skewed right distribution is one in which the tail is on the right side. Draw the histogram for the below data.
A distribution is right skewed if it has a tail on the right side of the distribution. If the histogram is skewed left the mean is less than the median. Whether a histogram is skewed left more of the data falls on right side or left side.
A random distribution lacks an apparent pattern. In this case the mean. 2 The horizontal scale represents the classes of quantitative data values from our frequency distribution.
For example the following histogram shows the number of students of Class 10 of Greenwood High School according to the amount of time they spent on their studies on. The following data represent the monthly phone use in minutes of one particular customer for the past 20 months. Whether a histogram is skewed left more of the data falls on right side or left side.
We see that the center of the values is2maxmin. This kind of distribution has a large number of occurrences in the upper value cells right side and few in the lower value cells left side. A graph of a frequency distribution that has the following characteristics.
The data are symmetric. On the right skewed distribution most of the data values occur on the left side with decreasing data on the right side. Below is the histogram in the problem.
A graphical presentation of the relationship between two variables scatter diagram a histogram is a graphical presentation of a frequency or rlelative frequency distribution a numerical measure of linear. It is also known as a positively skewed histogram. Classify each histogram as skewed to the left skewed to the right or approximately symmetric.
Right skewed distribution example. Note that the histogram appears to be roughly symmetric. Sometimes this type of distribution is also called negatively skewed.
A skewed distribution can result when data is gathered from a system with a boundary. And a distribution has no skew if its symmetrical on both sides. A distribution of this type is called skewed to the left because it is pulled out to the left.
Answer Explanation Correct answer. Big on left 3. 3 The vertical scale represents the.
1 It consists of bars of equal width drawn touching each other unless there are gaps in the data. Check out a sample textbook solution. In this histogram the bars of the histogram are skewed to the left side hence called a skewed left histogram.
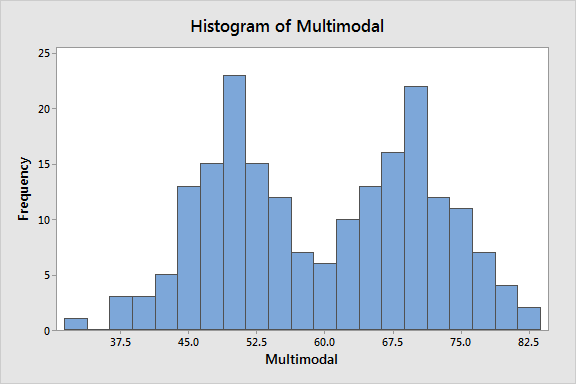
Using Histograms To Understand Your Data Statistics By Jim

Histogram Of Flood Loss For Building Structure From Surveyed Dataset Download Scientific Diagram

How To Describe The Shape Of Histograms With Examples Statology

Size Distribution Histogram For All Genotypes Studied Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment